
October 23, 2014 09:48 by
 Peter
PeterWhether you host in-house or with a managed Windows hosting provider, if you self-administer a web server it's sensible to understand that by default IIS 7.5 sets application pools to “time-out” when twenty minutes of inactivity. therefore if you don’t have a visitor to your website within twenty minutes the application pool can shut down those system resources. Then the next time a request comes into the site IIS7 can automatically restart the application pool and serve the requested pages.

This is an excellent way to preserve resources since each running application pool will place a certain quantity of overhead on the system. But, it conjointly implies that the primary request – the one that causes the application pool to restart – is incredibly slow. it's slow as a result of the method literally must begin, then load the desired assemblies (like .NET) then load the requested pages. betting on the size and complexity of your application, this would possibly simply be a couple of seconds or it'd take 30+ seconds (during which time a user would possible quit and move on to a different site).
If you wish to increase the length of the time-out setting, simply change it from the default of twenty to however several minutes you wish. you can also modify the setting to zero (zero) which effectively disables the timeout so the application pool can never shut down due to being idle.
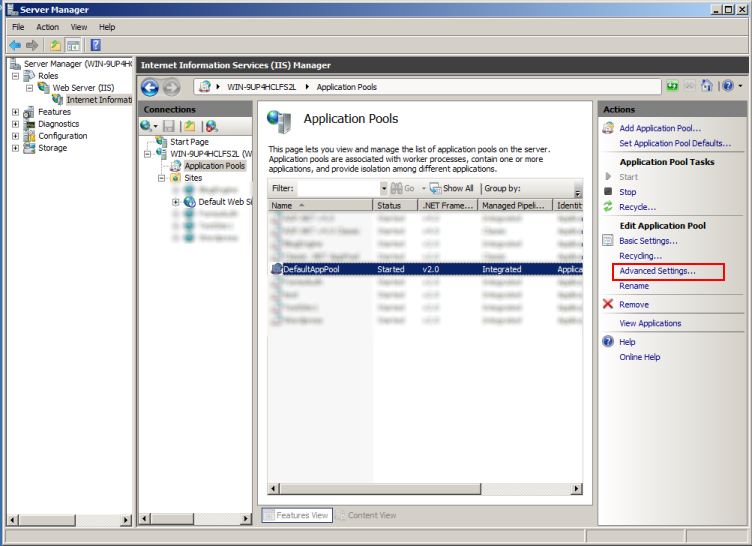
To make this change, open Server Manager; Expand the Roles node; Expand the web Server (IIS) node. Then click on the web Server (IIS) node; Expand the node along with your local server name; and click on the application Pools icon. You’ll then see a list of the application pools that are defined on your server. within the right-hand pane you’ll see an option for Advanced Settings -> click that.
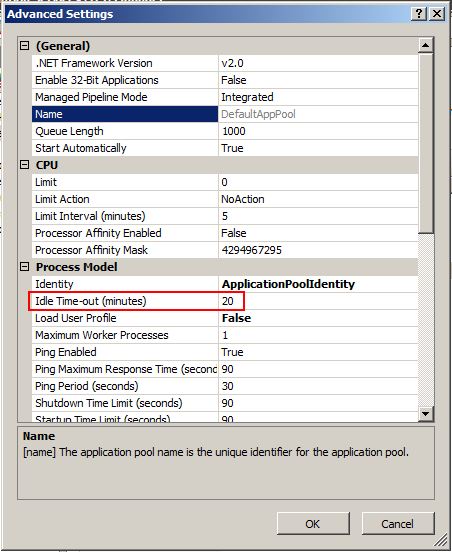
Once you see the Advanced Settings dialog box simply look for the Idle Time-out (minutes) property; click wherever the default “20″ is, and change it to no matter value you prefer.
This is only 1 of the many settings that may impact the performance, uptime, and functioning of your web site. If you don’t have the time or interest in learning and maintaining the various settings for a secure high-performing web server, you would possibly need to consider a totally managed windows hosting solution and let a trained and experienced administrator take care of the work for you.