The discussion is specific to IIS 7 and later versions. Let's start with version IIS 7.0. It has a built-in feature that is able to filter HTTP requests. If a request is found to have contents which are unacceptable to process the request, then it will block such request there, before proceeding to process a request by a web application. This feature is useful as a mitigation technique, for such SQL Injection vulnerabilities.
Prerequisite
At first, verify the IIS version that you are using currently. If you are using earlier than IIS 7.0, then update with the latest version before applying the following configuration.
Configuring the Request Filter
To create a global filtering rule for SQL Injection, we should follow the below steps:
Step 1
Open the run window by pressing keyboard key Windows key + R and copy and paste the following code
%systemroot%\system32\inetsrv\config\applicationhost.config
It will open the applicationhost.config file.
Step 2
In the applicationhost.config file, identify <requestFiltering> section. Under this section, configure for the reserve keywords or reserved special characters, like DELETE, CREATE, UPDATE, INSERT, --,',/* etc. in <denyStrings> section.
Configure the file extensions for which IIS server needs to be validated. The sample code is shown below:

Step 3
Now, to save the file, go to the File menu and choose Save option.
How does the above configuration behave in the IIS server?
With the above configuration settings, first of all, IIS will look at each incoming request for pages with .html, .aspx, or .asp extensions, to search for specific strings in the request's Query String. If the IIS server finds the specified strings, then IIS will block the request and return a 404: Not Found page to the client.
If you want to add a new file extension or change the existing file extensions in applicationhost.config file, you can add/remove the required file extensions in file Extension tags which lies in the <appliesTo> section. Whatever strings you are placing in the <denyStrings> section, the IIS looks for those strings. If it finds those, then it will block the request and return 404 error page to the client. You can add a new string, remove the existing string, or change the existing string, in the <denyStrings> section.
In fact, in IIS server, you may have hosted many web applications which are running in parallel.
Let's say, for one of the web applications, you don't want to deny any string for the incoming request. How will you handle such a scenario?
It is very simple. Create a rule in your application's config file, for which, you want to allow all such strings. If you create a rule in the application's config file, it will override the applicationhost.config file's rule. For instance, if you want to allow the string "end" for only a few applications, and for the rest of the applications, you want to deny such a string, then follow the below steps:
Step 1: Remove the <add string="end" /> entry from applicationhost.config file.
Step 2: Add the below code into the application's config file where you want to restrict the string "end":

Make a note -- the name for the filteringRule tag must and should be unique and it should not conflict with a name which is in the applicationhost.config file or/and the same name with any other web.config files in the path. And, it is also possible to limit the scope of filtering rules using location tags.
Procedure to check logs for SQL Injection attempts
You can check the SQL injection attempt logs in IIS W3SVC logs section. filteringRule rejects such SQL injection attempts and responds with a 404 status and with a substatus 19. You have to check these logs periodically to make sure that your rule is blocking such SQL Injections for the legitimate requests.
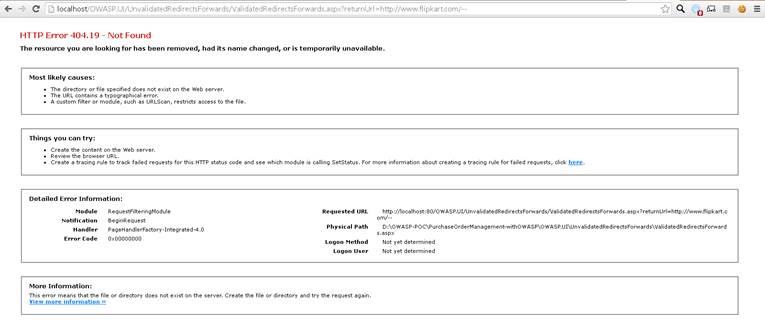
After the configuration changes made in the applicationhost file, if you give the followingURL request in your browser, the following output will show:
http://localhost/OWASP.UI/UnvalidatedRedirectsForwards/ValidatedRedirectsForwards.aspx?returnUrl=http://www.flipkart.com/--
Output
HostForLIFE.eu IIS 10 Hosting
HostForLIFE.eu is European Windows Hosting Provider which focuses on Windows Platform only. We deliver on-demand hosting solutions including Shared hosting, Reseller Hosting, Cloud Hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as a Service for companies of all sizes.
